How to use a commodity retro bonus in accounting and tax accounting? The size of the product retro bonus is calculated based on the total volume of goods supplied.
The article describes in detail retro bonus accounting and tax accounting. You will also learn how much to provide a retro bonus in different situations.
A bonus is usually understood as an incentive in the form of the delivery of an additional batch of goods to the buyer without payment. However, in fact, the provision of a product bonus is two interrelated business transactions:
Reflect the first business transaction in accounting in the manner prescribed for reflecting the discount.
Retro bonus accounting for the second operation, due to the fact that the amount of the restored debt, which was previously fully paid, is recognized as an advance received against a future (bonus) supply - charge VAT on the advance.
When supplying non-food products, any incentive, including when a retro bonus is provided, changes the price of the goods.
Since a decrease in the price of goods affects the seller’s tax obligations for income tax in past reporting (tax) periods, you can do one of the following:
When the price of goods changes, it is necessary to adjust the VAT tax base by issuing an adjustment invoice. The amount of VAT on the difference resulting from a decrease in the value of the goods can be deducted by the seller.
The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the Glavbukh System
Types of incentives
The concepts of “discount”, “bonus”, “Retro bonus” as a type of incentive are not defined by law.
A discount usually means a reduction in the contract price of a product. One of the forms of discounts includes incentives in the form of a reduction in the amount of the buyer's debt for the delivered goods.
A premium is a sum of money paid to the buyer for fulfilling certain terms of the contract, for example, for the volume of goods purchased. At the same time, the premium associated with the delivery of goods can also be a form of discounts (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 7, 2012 No. 03-07-11/364).
A bonus is usually understood as an incentive in the form of the delivery of an additional batch of goods to the buyer without payment. However, in fact, providing a bonus is two interrelated business transactions:
- providing a discount;
- sale of goods at the expense of the resulting accounts payable to the buyer. In this case, the amount of debt should be considered as an advance received (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 31, 2012 No. 03-07-15/118).
Discounts accounting
Discounts can be provided:
- at the time of sale or after the sale in respect of future sales;
- after sale - in relation to the goods sold.
If a discount is provided on a product that has already been sold, its reflection in accounting depends on when the discount was provided:
- before the end of the year in which the implementation took place;
- after the end of the year in which the implementation took place.
If the discount was granted before the end of the year in which the sale took place, adjust the sales proceeds in the period the discount was granted. In accounting, reflect such transactions as follows.*
At the time of sale (before the discount is provided):
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
– revenue from sales is reflected;
– VAT is charged (if the organization is a tax payer and the goods sold are subject to this tax).
At the time of discount:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
– revenue from previously shipped goods is reversed (by the amount of the discount provided);
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is reversed from the amount of the discount provided (based on the adjustment invoice).
This procedure is established by paragraphs 6, 6.5 of PBU 9/99.
If a discount was granted in the current year based on last year’s sales results, reflect the amount of the discount provided as part of other expenses in the current period on the date the discount was granted (clause 11 of PBU 10/99).
When identifying expenses of previous years in accounting, make the following entry:
Debit 91-2 Credit 62
– losses from previous years associated with the provision of a discount to the buyer (excluding VAT) were identified;
Debit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” Credit 62
– VAT is accepted for deduction from the amount of the discount provided (based on the adjustment invoice).
This procedure is established by clause 39 of the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting, the Instructions for the Chart of Accounts (account 91).
Retro bonus accounting
The provision of a bonus is accompanied by the reflection in the accounting of two business transactions:
- providing a discount on previously shipped goods;
- sale of goods against the resulting accounts payable to the buyer.
Reflect the first business transaction in the manner prescribed for reflecting the discount.
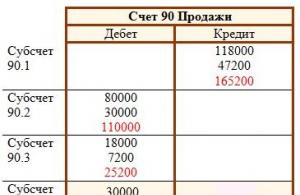
Let's look at retro bonus accounting using an example. Due to the fact that the amount of the restored debt, which was previously fully paid, is recognized as an advance received against a future (bonus) supply - charge VAT on the advance (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 31, 2012 No. 03-07-15/118) . In accounting, reflect the recognition of recovered accounts payable in advance and the sale of goods against this advance with the following entries:
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements for shipped products” Credit 62 subaccount “Settlements for advances received”
– the amount of the restored debt is recognized as an advance received against a future bonus delivery;
Debit 76 subaccount “Calculations for VAT on advances received” Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT”
– VAT is charged on the prepayment amount (recovered debt).
After shipping the bonus batch of goods, make the following entries:
Debit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT” Credit 76 subaccount “Calculations for VAT on advances received”
– VAT accrued on prepayment is accepted for deduction;
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements for shipped goods” Credit 90-1
– revenue from the sale of bonus goods is reflected;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is charged on proceeds from the sale of bonus goods;
Debit 90-2 Credit 41
– the cost of sold bonus goods is written off;
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements for advances received” Credit 62 subaccount “Settlements for shipped goods”
- prepayment has been credited.
Income tax
For the purpose of calculating income tax, an incentive (discount, retro bonus, bonus, gift), by agreement of the parties, can:
- do not change the price of the product;
- change the price of a product.
If the seller provides an incentive that does not change the price of the product, the income tax base does not need to be adjusted. Incentives of this kind must be taken into account as part of non-operating expenses (subclause 19.1, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). A similar point of view is reflected in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 19, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/668, dated September 27, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/506, dated April 3, 2012 No. 03 -03-06/1/175.
When using the accrual method, take into account expenses in the form of incentives provided to the buyer when calculating income tax in the reporting (tax) period to which they relate (Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the incentive under the terms of the agreement changes the price of the goods and is provided in the same reporting (tax) period in which the goods are sold, adjust the tax base for the profit tax of the current reporting (tax) period by the amount of the incentive (clause 7 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
If a decrease in the price of goods affects the seller’s tax obligations for income tax in past reporting (tax) periods, then you can do one of the following:
- submit updated income tax returns for previous reporting (tax) periods;
- do not submit updated returns, but recalculate the tax base and the amount of tax for the period in which the incentive was provided, and reflect this in the tax return for the same period;
- do not take any measures to adjust the tax base (for example, if the amount of overpayment is insignificant).
VAT
The procedure for accounting for incentives for VAT calculation purposes depends on the type of goods.
When supplying non-food products, any incentive, the occurrence of which is conditioned by the execution of the supply contract, regardless of its type and form, changes the price of the goods. This position is formulated in the resolutions of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated February 7, 2012 No. 11637/11 and dated December 22, 2009 No. 11175/09. In this case, when the price of goods changes, it is necessary to adjust the VAT tax base by issuing an adjustment invoice (subclause 4, clause 3, article 170, clause 13, article 171, clause 10, article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of VAT on the difference resulting from a decrease in the value of the goods can be deducted by the seller* (paragraph 3, paragraph 3, Article 168, paragraph 3, paragraph 1 and paragraph 2, Article 169, paragraph 13, Article 171, clause 10 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Sergey Razgulin,
Deputy Director of the Department of Tax and Customs Tariff Policy of the Ministry of Finance of Russia
“Sold a product for a certain amount - get a refund!” A retrospective bonus discount is an effective way to stimulate sales, widely popular in the field of trade abroad and actively spreading in Russia. We’ll talk more about this trade marketing tool in our article.
In worldwide practice, the popular term “rebate” is used in this regard. “rebate” – discount, concession. But in our country, representatives of retail chains most often use the term “retro bonus”.
Long-term partnerships between distributors and large suppliers are based on special contracts. They stipulate the conditions for receiving discounts and bonuses for fulfilling the sales plan for a certain period of time.
In this way, suppliers or manufacturers of goods motivate their distributors to fulfill the terms of the contract as actively as possible and sell the maximum number of goods to retail chains in the shortest possible time.
Relationships based on the payment of retro bonuses are not limited to the “manufacturer-distributor” scheme. Distributors themselves, after receiving discounts and bonuses, can further “stimulate” sellers in retail chains by giving part of the money received to the next participants in the supply chain.
Retro bonuses in retail chains: types and criteria for their accrual
 For distributors (or retailers), the conditions for receiving incentive payments, such as retrobonuses, may be different. But all conditions are always negotiated when concluding contracts for the supply of goods.
For distributors (or retailers), the conditions for receiving incentive payments, such as retrobonuses, may be different. But all conditions are always negotiated when concluding contracts for the supply of goods.
The most common option is when the counterparty receives retro bonuses upon fulfilling the sales plan. In other words, when a distributor sells a certain volume of goods (pre-agreed) or sells goods for a certain amount (for example, a million rubles or several hundred thousand).
The supplier or manufacturer provides such a counterparty with a discount or returns a certain amount of money (usually 10%). With the help of this type of retro bonuses, suppliers can stimulate sales of certain types of goods in retail chains or only in a certain segment.
Other suppliers provide their distributors or dealers with a rebate subject to financial discipline - that is, in the case of timely and full implementation of all payments under contracts, compliance with all terms of the transaction, etc. The bonus here may vary depending on the capabilities of the supplier.
Also, “rewards” in the form of retro bonuses can be provided to counterparties if they meet distribution indicators - that is, after assessing the quality of distributors’ work: analyzing how quickly the goods are transported, and the products are distributed in retail chains, etc.
The Business.Ru Retail program will help you obtain complete and reliable information about your business. You can always receive a detailed report that will show balances, turnover on the current account and cash register, and a breakdown of payments for each specific day. The program will also allow you to automatically issue incoming and outgoing cash orders in just a few clicks!
Retro bonus and its use in sales. Video
Forms for providing retro bonuses
 Payments of such incentive bonuses as retro bonuses can be made in different forms, and they are fixed within the framework of additional agreements. The main form of providing retro bonuses is the payment of cash bonuses for sales of goods in retail chains.
Payments of such incentive bonuses as retro bonuses can be made in different forms, and they are fixed within the framework of additional agreements. The main form of providing retro bonuses is the payment of cash bonuses for sales of goods in retail chains.
For example, if a retro bonus is paid as a percentage of the volume of goods sold in retail chains, the agreement states that when selling goods worth more than five hundred thousand rubles at the end of the quarter, the distributor receives a retro bonus in the amount of 5%.
That is, 25 thousand rubles will be “returned” to the counterparty. When providing bonuses under this scheme, both parties need to negotiate and agree on the time for accrual of bonuses and the timing of “motivating” payments.
The distributor's right to make purchases at better prices is another option in which rebates are provided by suppliers of goods. Here the distributor can purchase the required quantity of goods at discounted prices.
This offer is usually valid for a certain period of time. The parties also need to enter into an additional agreement and fix prices for goods.
Reducing prices is also a good option for providing retro bonuses for distributors of goods who distribute goods in retail chains. A discount on goods can be provided to the counterparty for a certain quantity or type of goods. It will be necessary to conclude an agreement between the parties confirming the buyer’s consent to change the cost of the purchased products.
Need to quickly respond to a supplier's price cut? This will be easy to do if the store's work is automated. With the program for automating the Business.Ru Retail store, you can not only quickly respond to market changes, but also receive a breakdown of payments for each specific day, issue cash receipts and debit orders, and much more.
Taxation of transactions on payments of retro bonuses
The provision and documentation of rebates in the financial statements of enterprises causes a lot of controversy among all market participants.
Many questions arise about the need to pay VAT on bonuses received by the distributor. Many supplier companies calculate the rebate by immediately increasing it by 18% VAT, but such conditions always cause a flurry of dissatisfaction - returning money in such quantities is simply unacceptable for suppliers.
According to experts, the taxation of retro bonuses also depends on what kind of goods are supplied - food or non-food. There are certain restrictions for food products in our country.
According to Russian legislation, if the price of a food product already includes VAT, then the bonus should be calculated based on this value of the product including VAT. In any case, the size of the retro bonus for any category of goods should not exceed 10% of the total cost of the goods delivered for sale by the supplier.
Hello! In this article we will talk about retro bonuses.
Today you will learn:
- Definition of retro bonus and their examples.
- For what purpose are they used?
- How to register retro bonuses. accounting
Example. According to the terms of the contract, goods worth 5 million rubles are purchased from the supplier. In total, we spent 150,000 rubles on logistics services and work with goods. In this situation, the maximum bonus amount can be 250,000 rubles. This is 5% of 5 million rubles. The compensation for services is 200,000, for goods – 50,000.
Products as a bonus
We have already noted that this is the most common type of bonus. Usually in this case the goods are delivered without requiring payment. But in this situation, tax obligations arise for VAT for the one who produced or sold the goods, as well as for gross income for the one who received them.
To avoid problems, you need to do the following:
- The contract should be drawn up taking into account all the subtleties of a legal nature;
- All transactions must be confirmed with official documents;
- The scope of work for which the bonus is awarded must also be certified with documents;
- At the time of bonus payment, use the concept of “payment for services that were provided” and not any other.
Bonus as % of product volume
If the bonus is planned to be paid in this form, then all the conditions for its accrual must be specified in the contract. At the same time, accounting specialists are very wary of such agreements.
The contract immediately mentions that the price of the product includes a bonus that will be paid as soon as a certain volume of purchases is reached. It also provides for notification and agreement by the parties of the moment when bonuses begin to accrue.
The notification is signed by both parties, which means that the bonus amount and the date of its payment have been agreed upon.
How to register in accounting and tax accounting
The registration of retro bonuses in financial statements currently provokes serious disputes between all market participants. Even accounting experts note that keeping records of these transactions is difficult. The most common question is the procedure for paying bonuses received by the distributor.
It happens that suppliers calculate bonuses by immediately increasing them by % VAT. But such a condition simply causes a storm of discontent - suppliers simply cannot return money in such quantities.
As experts say, the procedure for taxing bonuses will also depend on what specific product is supplied - food or non-food.
If the products are food grade, then there are some restrictions. For example, according to the laws of the Russian Federation, if the product is food and its price already includes VAT, then the bonus is calculated based on the cost including VAT.
Retro bonus and price reduction
Despite the fact that the retro bonus is formalized by an agreement with prices for goods that are provided to the recipient immediately. There are situations when they may be subject to revision.
Example. This can happen if the transaction was concluded during the tax period, and a discount was made on the product that will be shipped after this time.
But before using this bonus option, you need to understand what subtleties there are in the accounting design of this discount. It might even be worth consulting with experts on this issue.
In accounting, such a discount is issued using a negative invoice. This procedure has been completely legal since 2011.
The mechanism here is simple: the seller issues an adjustment invoice. The bonus recipient is then notified that the price has been reduced. And the recipient gives his consent to this in writing.
Only if both of these conditions are met, the seller can issue this discount as a type of bonus.
Options for reflection in accounting
The most commonly used option is when retro bonuses are applied to or towards the financial result obtained by the enterprise. Other suppliers, on the contrary, attribute bonuses to other company expenses, and reflect data on payment transactions in special accounts using accounting entries.
Conclusion
A retro bonus is a tool that can open up vast prospects for suppliers of goods and those who produce these goods. Motivation is a serious factor, and waiting for motivation can work wonders. But be as careful as possible when completing documents and reporting retro bonuses.
If the slightest mistake is made, it could lead to problems with the law.
Wholesale supply companies often offer discounts to their customers. In this case, discounts may also apply to shipments that have already taken place. And here it is extremely important to formalize everything correctly so that during a tax audit you do not encounter additional charges and fines.
One of the effective ways to attract customers and increase sales is to give them a discount. In practice, the most common discount is provided for achieving a certain volume of purchases. Discounts may vary. In this article we will look at discounts that affect the price of a product. Let us immediately make a reservation that such discounts cannot be applied to food products. Accordingly, in the article we will proceed from the fact that the subject of discounts that reduce the price are non-food products.
So, discounts can reduce the price of a product that has already been shipped or the price of a product that will be sold later (for example, when a certain volume of purchases is reached, the price of subsequent shipments is reduced by 3 percent). In the latter case, everything is quite simple: the shipment will be carried out immediately at a reduced price, that is, the price in the delivery note and invoice will be indicated taking into account the discount. Obviously, this option of providing discounts does not require any subsequent adjustments in accounting and documents. Accordingly, there is no expense in the form of discounts for the seller, and no income for the buyer.
VAT and invoices
But in the case of discounts on “accomplished” shipments (retro discounts), the situation is more complicated. Since VAT was initially calculated on the price “before the discount”, the question arises: is it necessary to reduce the previously calculated VAT and submit an updated VAT return for that period?No no need. And the adjustment in terms of VAT obligations will be achieved by applying a deduction. According to paragraph 13 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the seller has the right to deduct the difference between the tax calculated before the discount was granted and the tax calculated after the discount was granted. In this case, the seller who “reduces” the price of previously shipped goods will have to draw up an adjustment invoice (Clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This document will be the basis for a deduction from the seller (clause 10 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, the adjustment invoice must be recorded in the purchase ledger.
Single adjustment
It often happens that a discount applies to several deliveries made in past periods at once. In this case, there is no need to prepare a separate adjustment invoice for each “accomplished” delivery. Tax legislation allows for the preparation of a single adjustment invoice (clause 5.2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In such a situation, the adjustment invoice should indicate the numbers and dates of all invoices, separated by commas.In a single adjustment invoice, in particular, it is necessary to indicate:
- serial numbers and dates of preparation of all invoices, for which a single adjustment invoice is compiled;
- the quantity of goods (works, services) on all invoices before and after the quantity is clarified;
- the cost of the entire quantity of goods (work, services) for all invoices without VAT and with VAT before and after the changes made;
- the difference between invoice indicators before and after changes in the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered).
It must be said that the department previously spoke differently. The Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 12, 2013 No. 03-07-09/37680 stated that tax legislation does not provide for the reflection of aggregate indicators for several supplies in single adjustment invoices.
Recovering VAT from the buyer
Let's consider the actions of a buyer who received a retro discount. Before receiving the discount, the buyer capitalized the goods and accepted the “input” VAT for deduction. After some time, they received a discount that reduced the price of the previously purchased product. The buyer must restore the VAT corresponding to this discount (subclause 4, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).VAT recovery is carried out by the buyer in the tax period in which the earliest of the following dates falls:
- the date of receipt by the buyer of primary documents for a change in the direction of reducing the cost of purchased goods;
- the date the buyer receives the adjustment invoice.
“Converting” a discount into an advance
It is important whether the buyer paid for the goods at the time the discount was granted. If the discount is provided after the buyer has paid in full for the goods, the supplier:- or returns to the buyer the difference between the price of the product taking into account the discount and the actual payment amount;
- or keeps it in order to subsequently use it to pay for future deliveries to the same buyer.
Officials believe that it is necessary to include the amount of the “advance payment” in the VAT tax base in the period when the cost of the goods (work, services) supplied has decreased. After all, it was then that the overpayment arose. And as a general rule, the VAT base is determined by the earliest date: the day of shipment or the day of payment (partial payment).
Tax accounting for the seller
Providing discounts leads to the need to make changes to the income tax of sellers. How can they reflect the retro discount in tax accounting?The Tax Code of the Russian Federation has a provision that discounts should be included in non-operating expenses (subclause 19.1, clause 1, Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, this provision applies to discounts that do not affect the price of the product (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated May 25, 2012 No. 16-15/046114@, Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the North Caucasus District dated May 8, 2015 No. F08-2247/2015 on the case No. A53-27549/2013). Whereas we consider discounts that affect the price of previously reflected supplies.
Does this mean that the seller will have to adjust prior period earnings and submit an amended income tax return? No, it doesn't mean that. The fact is that the provisions of paragraph 1 of Article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allow not to adjust past periods, but to take into account changes in the current period if an error led to excessive payment of tax. Since providing a discount leads to excessive payment of income tax for the previous period, the seller can take the discount into account in the current period without resorting to drawing up “clarifications”. Such clarifications follow from Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 06.23.10 No. 03-07-11/267, dated 05.22.2015 No. 03-03-06/1/29540.
Thus, the seller will reflect the discount in tax accounting as part of non-operating expenses as a loss of previous tax periods identified in the current reporting (tax) period.
Tax accounting for the buyer: clarification or risks?
The buyer receiving a discount that reduces the price of a previously purchased product will entail a change in the purchase price reflected in tax accounting. Such clarifications are given in Letter dated January 16, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/13. At the same time, officials add that the buyer does not have income in tax accounting when receiving such a discount.But you can change the purchase price only for those goods that are in the buyer’s warehouse at the time the discount is received, that is, for goods that have not yet been deregistered. Or if the discount and sale occurred in the same reporting period. In these situations, changing the data on the purchase price will not entail the preparation of an updated income tax return, because these goods have not yet fallen into the “expenses” part. And if they do, the company can correct the data without much difficulty before preparing the income tax return.
What if the discount was received after the reporting period in which the “discounted” goods were sold has ended? Unfortunately, there is no clarity regarding this situation.
On the one hand, the company seems to have to submit an update on the income tax for the period of sale of goods, because the data included in the primary declaration was before the price reduction. But on the other hand, companies are required to submit an updated declaration only if errors and distortions are made. It is not entirely correct to say that at the time of writing off the cost of expenses the company made a mistake or distortion, because at that time it acted strictly in accordance with the available documents on the cost.
Unfortunately, there are no recent official clarifications that shed light on this situation. There is only the old Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 20, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/137, which considers the situation when a company receives a discount on purchased materials (not goods), and at the same time uses the method of valuing raw materials and supplies at average cost . Officials explain that when the price changes, the buyer must recalculate the average cost of the corresponding material assets in tax accounting, starting from the period of capitalization until the moment of write-off. Extending the conclusion given in the letter to the situation with the purchase of goods, it can be assumed that officials are in favor of the buyer submitting an updated income tax return.
At the same time, there are oral explanations from certain officials from the Ministry of Finance who believe that the buyer can include the discount amount in non-operating income of the current period, even if, by agreement with the supplier, the discount changes the price of the goods supplied. Such consultations can be found in some media and at seminars. This method is certainly convenient for companies. And for some companies, having a huge range of products may be the only option. After all, with regular discounts on different assortments of goods, it is quite difficult to track which specific “outdated” unit of goods the discount applies to.
In addition to being convenient, this option is also profitable. After all, then you won’t have to pay extra tax on the updated declaration and pay penalties. However, there is no guarantee that inspectors will support this method of accounting during inspection. Oral explanations from officials, as they say, “cannot be added to the case.”
Thus, each organization, taking into account the existing risks, independently decides what to do.
We come across the concept of “bonus” both in the everyday sphere of life and in the work sphere. The nature of the bonus is clear - these are certain additional benefits received by a person in the form of incentives, bonuses or allowances. The essence and purpose of bonuses is simple - to motivate, encourage, attract attention in order to form permanent relationships, lasting connections, trade and exchange processes. However, in Russia there is such a thing as a “retro bonus”. What a retro bonus is in trading and how it works will be discussed below.
What is it and how does it work
This concept is used mainly by Russians in the process of trade and exchange relations. In global trade terminology, the definition most often used is “rebate” from the English rebate. In its essence, a retro bonus is nothing more than a payment or payment that is made by making the following variations:
- cash payment, which represents the return of a certain amount from the cost of a completed purchase and sale transaction;
- provision of goods for full use free of charge;
- option - the right of a client, or a third party, to enter into a transaction for the purchase and sale of goods within a certain time at a specially established price.
Bonus products as retro bonuses
The simplest and most frequently used in trade and exchange relations is this type of bonus, such as free delivery of goods. But this type of trade relationship entails the emergence of certain tax obligations for value added tax for the manufacturer of goods or seller and tax obligations for gross income for the recipient.
To avoid tax audits and the difficulties that arise during them, you need to follow these steps:

Legal registration
A retro bonus is, first of all, a relationship that arises between two parties for the purpose of paying the bonus obligations of one party to the other. Therefore, the fact of legally correct registration of such relations is important.
In legal practice, bonuses are remunerations that are paid to a party as a result of the provision of certain services. To significantly simplify tax accounting, it would be more correct not to tie such transactions to the main purchase and sale agreement, but to formalize them as separate eligible agreements.
Practice
Practice is exactly what helps you understand what a retro bonus is. An example of use in marketing is the simplest and most understandable. For example, a party that has received a marketing service such as collecting or distributing information, conducting promotions, or merchandising issues a retro bonus to the party that provided this service in the form of providing free goods upon completion of the action.

Calculation
If a retro bonus is nothing more than a percentage of the volume of products sold, then the main conditions for its provision must be described in a consignment agreement, which is concluded between the two parties between whom trade and exchange relations have arisen. Drawing up such agreements and calculating retro bonuses is a rather labor-intensive process for the accounting department of enterprises, since the following information is necessarily mentioned in the agreement:

The practice of reducing the price in retro bonus relationships
Despite the fact that a retro bonus is a legally formalized relationship in the form of a signed agreement, which specifies the price of goods provided to the recipient of the bonus, in practice there are cases when the price of goods already shipped and delivered to the recipient can be revised. This happens when a transaction for the provision of goods was concluded during the tax period, and the company makes a post-discount on the price of goods that are shipped after the tax period. However, before using this type of retro bonus, you need to understand the intricacies of registering such a discount in the accounting department. In addition, it is better to ask knowledgeable people to show a sample of a retro bonus, so as not to run into problems.

In accounting, such a retro discount is issued through a negative invoice. Since October 1, 2011, such accounts have been fully legalized, and their use is legal and permitted by law. The mechanism for issuing a discount is simple: first, the seller of goods issues an adjustment invoice. The second main condition is the fact of notification of the recipient about the price reduction, documentary evidence of his consent to carry out this operation. Only if the two above-mentioned grounds are present, the seller has the right to issue a retro discount as a special type of retro bonuses.
In general, the practice of providing retro bonuses in trading is a simple and necessary thing, however, before applying it, it is necessary to enlist the support and awareness of the accounting department, because if the wrong approach is used, a good deed can turn out to be completely opposite.